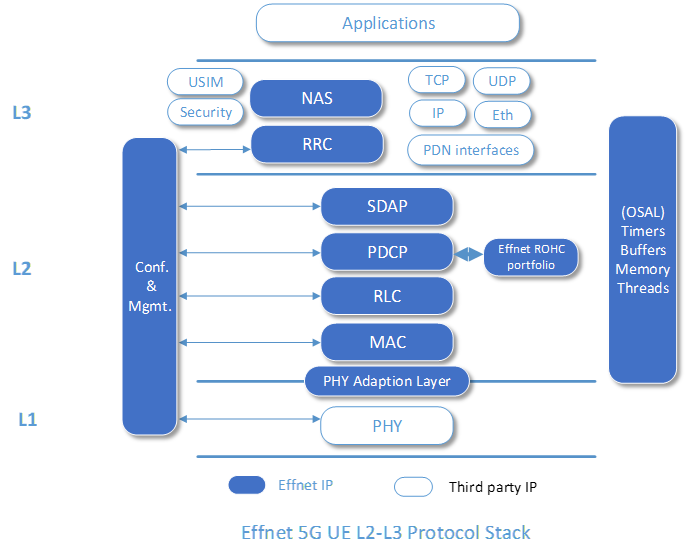
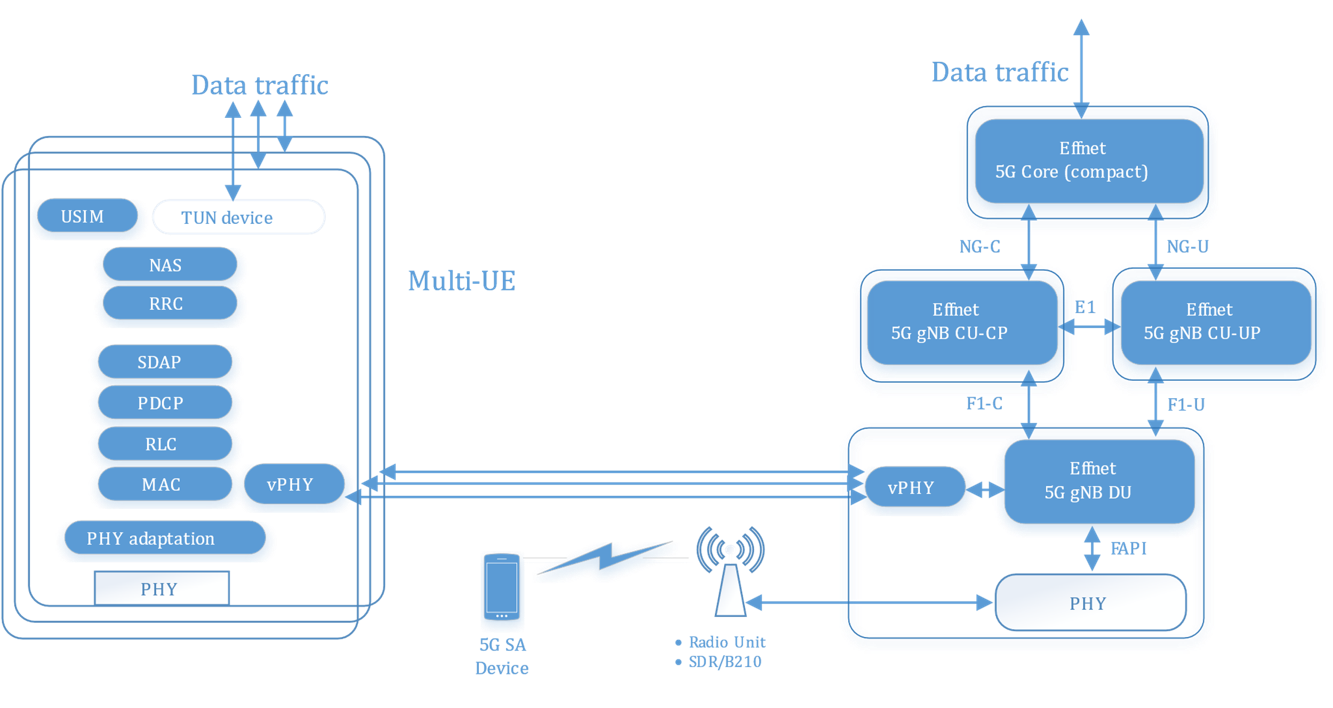
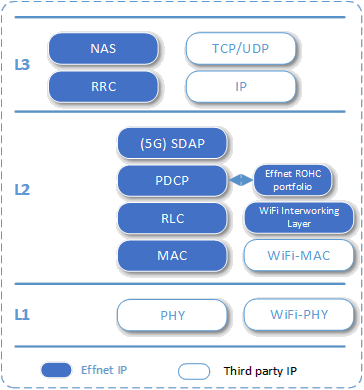
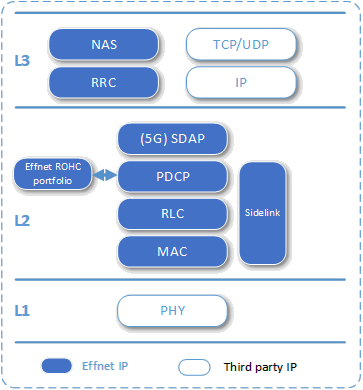
Effnet 5G UE/CPE L2-L3 Protocol Stack
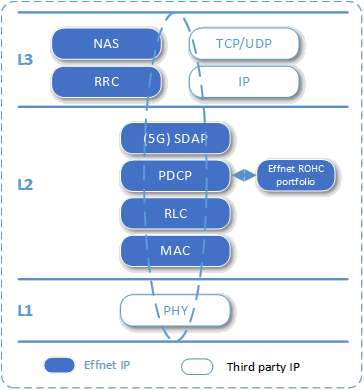
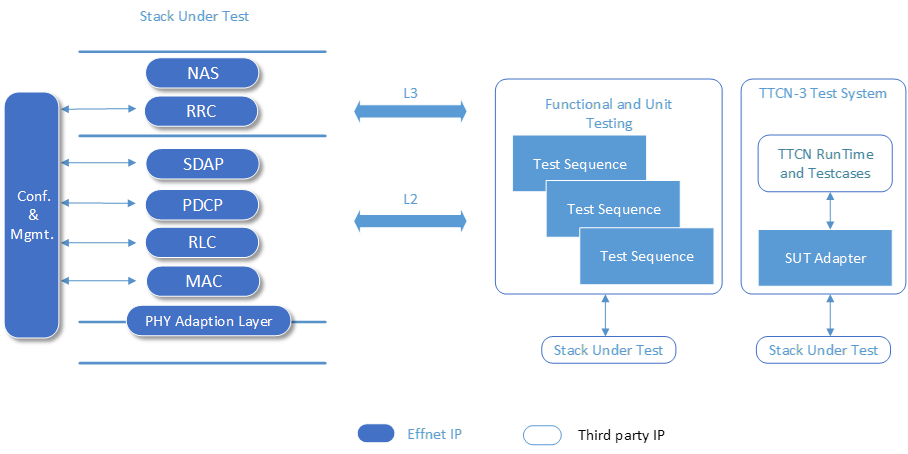
Effnet provides a highly portable and modular 5G L2-L3 UE protocol stack suitable for use in many applications and markets. Thanks to its PHY adaptation layer it can be integrated with L1 from different vendors.
Target applications/markets
- Customer premises equipment (CPE), industrial routers, modules
- Fixed wireless access
- 5G IoT and Industrial IoT
- 5G V2X (Vehicle to Everything)
- Test systems
Licensing to
- OEMs/ODMs/modem manufacturers
- Protocol stack developers
- System integrators